Fill Out a Valid West Virginia Estate Form
In the intricate journey of estate management following the demise of an individual, West Virginia provides a structured path to ensure a clear and lawful transition of assets through its Estate Appraisement & Nonprobate Inventory Forms, a guide instantiated by the Tax Account Administration Division of the West Virginia State Tax Department for decedents passing on or after July 13, 2001. Charged with the duty of easing representatives into their roles, this booklet delineates the obligations required under West Virginia law, including estate administration, and the obligatory filing of detailed appraisements and inventories regarding both probate and nonprobate assets within the decedent's county of domicile. Representatives, whether administrators without a will or executors with one, shoulder the responsibility to appraise and file inventories of the decedent’s real and personal estate, a fiduciary duty to settle the decedent’s debts and allocate the remainder property accordingly. The necessity to navigate these responsibilities within 90 days of qualification highlights the gravity and impending urgency that estate representatives must accord to the process. Additionally, elucidated within the booklet are the comprehensive steps from reading the initial instructions to the final delivery of the filled forms to pertinent authorities, with explicit mandates on reporting real estate, personal properties, and the respective obligations concerning state and federal tax requirements. This framework underscores a meticulously designed protocol aimed at simplifying the formidable process of estate administration.
Sample - West Virginia Estate Form

West Virginia
EstatE appraisEmEnt & nonprobatE inVEntory
Forms and instructions
his booklet is furnished by the Tax Account Administration Division of the West Virginia State Tax Department for use in iling the Appraisement and Nonprobate Inventory Forms for estates and decedents dying on or after July 13, 2001.
an important mEssagE For EstatE rEprEsEntatiVEs:
When a person dies an estate is created. An estate includes property which the decedent owned. he law requires that someone must administer the estate by iling the Appraisement and Nonprobate Inventory Forms within 90 days of qualiication and completing inal settlement in the decedent’s county of domicile. administration is the process of paying the decedent’s outstanding debts and distributing the remaining property. he person in charge of the administration is called an administrator (if there is no will) or an executor (if there is a will). Also, because the administrator or executor holds a position of trust, a person with either title is often called a iduciary. If there is no will, the decedent is said to have died intestate, and his property passes by statutes called the laws of intestacy. hus you will also see the phrase “transfers by will or intestacy”.
this booklEt is intEndEd to hElp you With thrEE dutiEs
rEquirEd by WEst Virginia laW:
•he administration of the estate (also called the process of probating the estate).
•he iling of an inventory of ALL real estate and probate property with the County Clerk’s Oice using Form ET 6.01 (recorded with the County Clerk’s oice).
•he iling of an inventory of nonprobate personal property with the County Clerk’s Oice using Form ET 6.02 (not recorded with the County Clerk’s oice).
Beginning the legal process to settle the business and personal afairs of a decedent involves a series of steps, outlined below and explained in detail in this booklet:
STEp 1 |
rEAD ThESE INSTruCTIONS. |
STEp 2 |
COmpLETE ApprAISEmENT FOrm ET 6.01. |
STEp 3 |
COmpLETE NONprOBATE INVENTOry FOrm ET 6.02 (IF rEquIrED). |
STEp 4 |
mAIL Or DELIVEr ThE FOrmS TO ThE prOpEr AuThOrITIES |
a more detailed look at these four steps begins on the next page.
WV Estate Appraisement and Nonprobate Inventory – Forms and Instructions – page 1

stEp 1: rEad thEsE instruCtions For Filing Form Et 6.01 and Form Et 6.02.
you should read these introductory instructions completely before beginning any work on the forms. you will notice references to other speciic instructions that also must be understood before completing related parts of the forms.
To qualify as iduciary, a person must visit the oice of the Clerk in the courthouse of the county where the decedent lived. Any person who has an interest may administer the estate. however, the husband or wife of the decedent is given preference and then other distributees (others who are entitled to a share of the estate) are considered. If no distributee applies within thirty days after the date of death, one or more creditors or any other person may be appointed. If there is a will that names an executor, then the named person has the right to serve. In any event, the Clerk is the irst person to visit, and he or she will determine who can qualify as iduciary.
his booklet is designed to help the iduciary administer the estate and ile the Appraisement and Nonprobate Inventory Forms. he iduciary is required under oath to list and appraise on the enclosed Appraisement Form (ET 6.01) all nonprobate and probate real estate and all other probate assets owned by the decedent at its fair market value on the date of the decedent’s death. he iduciary is required to complete the Appraisement and return the original and two (2) copies thereof (with all attachments) to the Clerk within 90 days of qualiication. he original Appraisement, and its attachments, must be recorded by the Clerk.
For every decedent who owned or had an interest in any nonprobate personal property, the iduciary shall, under oath, list and appraise on the enclosed Nonprobate Inventory Form (ET 6.02), all tangible and intangible nonprobate personal property owned by the decedent or in which the decedent had an interest, at its fair market value on the date of the decedent’s death. If a Nonprobate Inventory Form (ET 6.02) is required to be iled, the iduciary must complete the form and return the original to the Clerk within 90 days of qualiication.
stEp 2: ComplEtE Form Et 6.01
part 1: general information Questionnaire. his information is used to establish that an estate actually does exist, and to provide the information necessary for the Clerk and the State Tax Department to process the appraisement, determine if the estate is subject to Estate Tax, and approve the inal distribution and closing of the estate.
Question instructions for form et 6.01
ABe sure to include the decedent’s complete name. Any other names by which the decedent was known should be shown after the complete name.
CBe sure to write the date of death as shown on the decedent’s death certiicate.
address to which he would return if released from the care facility.
Ihe Internal revenue Service requires the iling of a Federal Estate Tax return (Form 706) for the estate of every citizen of the united States whose gross estate at the time of death was larger than the amount of the federal exemption equivalent. he exemption equivalents are:
year of death |
Exemption Equivalent |
2004 through 2005 |
$1,500,000 |
2006 through 2008 |
$2,000,000 |
2009 |
$3,500,000 |
2010 through 2011 |
$5,000,000 |
2012 |
$5,120,000 |
2013 |
$5,125,000 |
2014 |
$5,340,000 |
|
|
For further information concerning federal estate tax requirements, contact your local IrS oice or call their
L & m Be sure to provide the complete mailing address and phone number for both the iduciary and preparer. If the address or phone number shown is incorrect or incomplete, it may be diicult to contact you if additional information is necessary to process the appraisement.
part 2: Questionnaire of nonprobate real estate. Nonprobate real estate includes any real estate that does not pass by the will or the laws of intestacy. his includes real estate jointly held with right of survivorship, real estate held under a trust agreement or contract, life estates, or powers of appointment. his real estate passes directly to the speciied persons at the date of death according to these speciic terms and thus is not subject to administration, but is included in the gross estate for estate tax purposes. If there is any nonprobate real estate, additional information is required to be furnished as part of the appraisement to fully describe the transfer, including the type of transfer, recipient and relationship to the decedent, and the description and value (as of the date of death) of the transferred property. he Inventory of Nonprobate real Estate is included with this booklet for your convenience. he appraisement is incomplete if the iduciary fails to include this information. also, you must provide the description of all out of state real estate, including the appraised value.
Note: Oil, gas, coal and other natural resource holdings are considered as real estate for the purpose of this inventory. hese holdings should be listed either on part 2 as nonprobate real estate, or on Schedule A of part 4 as probate real estate.
part 3: summary of probate assets. All probate assets (assets in decedent’s name only) must be on record at the Clerk’s oice prior to being transferred to the heir or beneiciary. his property will be transferred under the terms of the decedent’s will, or under the laws of intestacy if the decedent died without a will. until the assets are transferred, they are required to be managed (administered) by the iduciary. probate assets are to be described
WV Estate Appraisement and Nonprobate Inventory – Forms and Instructions – page 2

in detail in part 4 of the appraisement; the total value of each type of property will then be entered in part 3.
part 4: inventory of probate assets. A complete description of ALL probate assets is to be provided in part 4. real property should include the description used on the real property tax tickets as to county, district, and physical location and description of the property. he personal representative must list the value of each probate asset at the date of the decedent’s death. Total the values of all property shown in each schedule of part 4 and enter the total on the appropriate line of part 3 (Summary of probate Assets).
sChEdulE a: INCLuDE the clear legal description of any rEAL ESTATE. he description must provide suicient information to identify the property and include, where applicable, the county, district and lot size (number of acres). Include the assessed value of the real estate as shown on the decedent’s property tax receipt. If the decedent has been given the homestead Exemption, the full assessed value (without the deduction for homestead Exemption) must be shown. Include the full appraised value of the decedent’s interest in the real estate. When the decedent owned a fractional interest, list the full value of only his or her share (for example “½ interest $000.00). he appraised value must be the mArKET VALuE as of the date of death. market value is deined as the price a willing buyer would pay willing seller for the property. his value must be used regardless of whether the property will be kept or sold by the beneiciaries. he date the property was acquired by the decedent should also be shown. also, you must provide the description of all out of state real estate, including the appraised value.
Note: Oil, gas, coal and other natural resource holdings are considered as real estate for the purpose of this inventory. hese holdings should be listed on Schedule A of part 4 as probate real estate, or on part 2 as nonprobate real estate.
IF ThE DECEDENT OWNED rEAL ESTATE IN mOrE ThAN ONE COuNTy, an appraisement containing the description of the property must be iled in each county where real estate is located. he various counties should all be listed in part 1: General Information questionnaire (question h).
sChEdulE b: INCLuDE the type and market value of all TANGIBLE pErSONAL prOpErTy. Tangible personal property consists of assets which you can touch, that is, which can be possessed physically, including goods, wares, merchandise, furniture, personal efects, and automobiles.
sChEdulE C: INCLuDE all bonds and securities OThEr than corporate stock, the date of purchase and market value as of the date of death.
sChEdulE d: INCLuDE corporate stock of every kind. List the name of the company, the number of shares, value per share and the total market value of the decedent’s interest as of the date of death. place a check mark in the “CLOSELy hELD” column if the corporation is NOT listed on a stock exchange.
sChEdulE E: INCLuDE any intangible personal property (cash, bank accounts, certiicates of deposit, notes, accounts receivable, etc.) owned by the decedent. Show a description of the property and include the market value as of the date of the decedent’s death.
sChEdulE F: INCLuDE any other assets by the decedent at the time of death EXCEpT those reported on the NONprOBATE INVENTOry FOrm (ET 6.02) of the estate. If the decedent had life insurance policies payable to the estate (rather than to individual beneiciaries), they must be included on this schedule.
part 5: beneiciaries. A complete list of the individuals who will inherit under the terms of the will, or through the laws of intestacy, is required. he relationship of each recipient to the decedent must also be provided.
part 6: oath of fiduciary. his oath must be completed in the presence of a notary. It is a sworn statement that the iduciary has made every efort to completely list and describe the assets of the estate. he signature of the iduciary and the notary must be aixed to the original appraisement. An appraisement which does not have original signatures will not be accepted by the Clerk. After completion of this oath, the iduciary must obtain two (2) complete copies and deliver the appraisements to the proper authorities, who will complete the remaining parts.
part 7: approval of fiduciary Commissioner/fiduciary supervisor. he Fiduciary Commissioner or Fiduciary Supervisor will complete and sign the appraisement in this section after he determines it to be accurate and complete.
part 8: Clerk of the County Commission. he Clerk will complete this section when the appraisement is recorded.
stEp 3: ComplEtE Form Et 6.02 (iF rEquirEd). For every decedent who owned or had an interest in any nonprobate personal property, the iduciary shall, under oath, list and appraise on the enclosed Nonprobate Inventory Form (ET 6.02), all tangible and intangible nonprobate personal property owned by the decedent or in which the decedent had an interest, at its fair market value on the date of the decedent’s death. he nonprobate personal property to be included on the Nonprobate Inventory Form includes: 1) personal property held as joint tenants with right of survivorship; 2) personal property payable on death to others; 3) personal property held by the decedent as a life tenant; 4) life insurance to named beneiciaries; 5) powers of appointment; 6) annuities; 7) transfers during the decedent’s life; 8) transfers in trust; 9) taxable gifts; and 10) all other nonprobate personal property includible in the federal gross estate of the decedent.
he iduciary is required to make the Nonprobate Inventory Form available for inspection by or disclosure to: 1) any heir at law or beneiciary under the will; 2) a creditor who has timely iled a claim against the estate with the iduciary commissioner or iduciary supervisor; 3) any party who has iled a civil action in any court of competent jurisdiction in which any assets of the decedent is in issue; or 4) the attorney for the estate or its personal representative or the
part 1: general information Questionnaire. Be sure to complete the General Information questionnaire of the NONprOBATE INVENTOry FOrm. his information should be the same as reported on the Appraisement.
part 2: Questionnaire of nonprobate personal property. Answer each question in this summary. If a question does not
WV Estate Appraisement and Nonprobate Inventory – Forms and Instructions – page 3

apply to the decedent, mark the “NO” box and enter zero for the market value for that line. For any “yES” answer, remember to complete part 3, Inventory of Nonprobate personal property. Be sure to enter the total of ALL nonprobate personal property on line 11 of part 2.
part 3: inventory of nonprobate personal property. For each “yES” answer in part 2, you must provide in part 3 the property description, the name(s) of the person(s) receiving the property and their relationship to the decedent, and the fair market value at the date of death.
part 4: oath of fiduciary. his oath must be completed in the presence of a notary. It is a sworn statement that the iduciary has made every efort to completely list and describe the assets of the estate.
stEp 4: mail or dEliVEr thE Forms to thE propEr authoritiEs
in counties where there is a fiduciary supervisor, the iduciary must deliver an original completely executed appraisement and two (2) copies thereof (including any attachments) to the Fiduciary Supervisor. he Fiduciary Supervisor will in turn deliver an original and one (1) copy of the appraisement to the Clerk’s oice after completing part 7. After completing part 8, the Clerk will admit the original appraisement (and its attachments) to record.
incountieswherethereisnofiduciarysupervisor,theiduciary must deliver an original completely executed appraisement and two (2) copies thereof (including any attachments) to the Clerk’s oice. After completing part 8, the Clerk will admit the original appraisement (and its attachments) to record and forward one
(1)copy of the appraisement to the Fiduciary Commissioner (if reference to a Fiduciary Commissioner is required).
he Fiduciary Commissioner or Fiduciary Supervisor cannot assist you in the preparation of a tax return (if one is required) or of any other report on which he must eventually pass judgment. he is also prohibited from practicing law in connection with an estate that has been referred to him (West Virginia Code
he following statements and deinitions are provided to help you understand the questions asked on Form ET 6.01 and Form 6.02.
power of appointment is authority conferred by one person (called the “donor”) by deed or will upon another (called the “donee”) to select the person who is to receive and enjoy real or personal property after the death of the donor or the donee, or after the termination of an existing right or interest.
gifts made Within hree years prior to date of death may be presumed to have been made in contemplation of death and must be listed.
life Estate means the decedent during his lifetime transferred real property by deed, grant, sale or gift but reserved an interest in the property for the remainder of his lifetime. If the recipient did not pay an appropriate consideration for the transfer of the remainder interest, the entire date of death value must be listed for estate tax purposes. If the decedent was granted a life estate or dower interest in real property, the life estate or dower interest expires at death and has no value for estate tax purposes. however, this property should still be listed to clear title.
right of survivorship means that the decedent’s share of the property automatically goes to the remaining owner(s) after his death. he entire market value of survivorship property must be listed with no exclusions or deductions.
payable on death means an asset owned by the decedent which is paid to another at the time of the decedent’s death.
If the decedent transferred assets to a trust during his lifetime, a complete inventory (with the market values) of the assets must be included.
Transfers due to the terms of an annuity, investment contract, or pension plan payable on account of death to named beneiciaries, or to a trust for the beneit of any individual must be listed. he value listed should be the date of death lump sum value of the annuity, available by contacting the sponsoring company.
IF yOu hAVE quESTIONS, INFOrmATION rEGArDING SpECIFIC CIrCumSTANCES IS AVAILABLE FrOm ThE CLErK OF ThE COuNTy COmmISSION, FIDuCIAry COmmISSIONEr, Or FIDuCIAry SupErVISOr. yOu mAy ALSO NEED TO CONTACT AN ATTOrNEy, ACCOuNTANT Or TruST OFFICEr FOr mOrE INFOrmATION.
WV Estate Appraisement and Nonprobate Inventory – Forms and Instructions – page 4
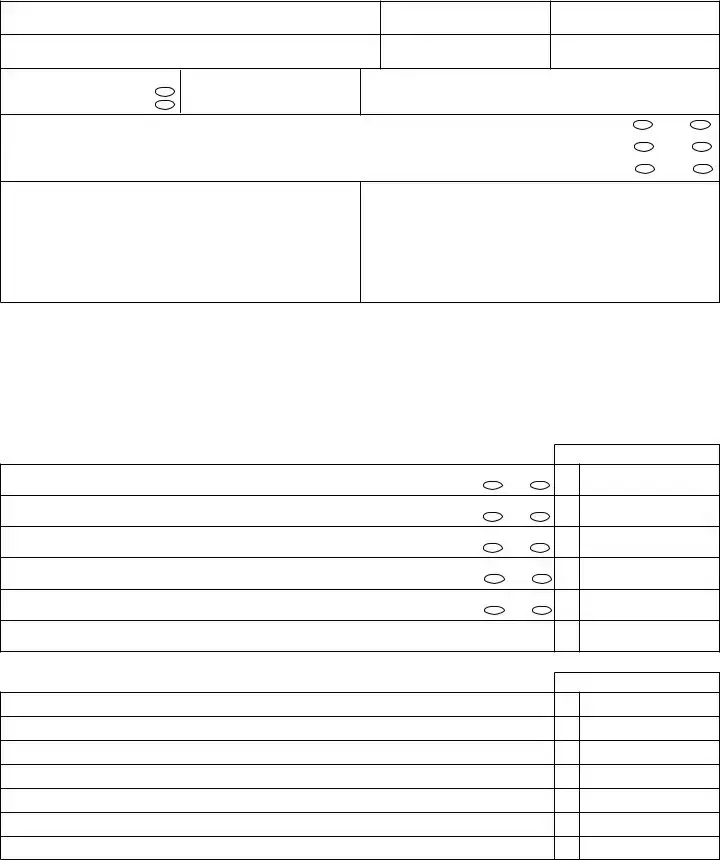
Form ET 6.01 |
ApprAisement of the estAte |
Rev. 06/14 |
for DeceDents Dying on or After July 13, 2001 |
|
|
pArt 1: generAl informAtion QuestionnAire
A. Decedent’s Name
B. Social Security Number
C. Date of Death
D. Decedent’s Residence at Death
E. State
F. County
G. Marital Status at Death |
Name of Surviving Spouse |
Married |
|
Single, Widow(er) or Divorced |
|
H. West Virginia Counties Where Decedent Held Real Estate.
I. Will this estate be required to ile a Federal Estate Tax Return form 706 (see instructions on page 2)? |
YES |
NO |
|
|
|
J. Will this estate be required to ile the nonprobate inventory form et 6.02 (see instructions on page 3)? |
YES |
NO |
|
|
|
K. Did the Decedent leave a Will? |
YES |
NO |
L. Fiduciary’s Name and Mailing Address (include zip code)
________________________________________________
________________________________________________
________________________________________________
________________________________________________
Fiduciary’s Phone Number:
M. Preparer’s Name and Address CPA  Attorney
Attorney 
________________________________________________
________________________________________________
________________________________________________
________________________________________________
Preparer’s Phone Number:
pArt 2: QuestionnAire of nonprobAte reAl estAte
Answer each of the following questions concerning the decedent’s interest in NONPROBATE REAL ESTATE.
if you answer “yes” to any question below, you must complete the attached inventory of nonprobate real estate provided with this form which shows:
a.the type of transfer(s) with reference to the question number below;
b.name(s) of the person(s) with an interest in the real estate as joint tenant or transferee;
c.relationship to the decedent of ALL above named persons;
d.market value at the date of death; and
e.description of the real estate including assessed value.
|
|
|
|
mArket VAlue |
1. |
Did the decedent own an interest in any real estate as joint tenant with right of survivorship? |
YES |
NO |
1 |
2. |
Did the decedent transfer an interest in any real estate without adequate consideration within three years prior to |
|
|
|
|
date of death? |
YES |
NO |
2 |
3. |
Did the decedent own an interest in any real estate in an inter vivos trust (living trust) arrangement or in which the |
|
|
|
|
decedent retained the right of use and enjoyment? |
YES |
NO |
3 |
4. |
Did the decedent own an interest in any real estate in which the decedent retained a power of appointment, |
|
|
|
|
whether special or general? |
YES |
NO |
4 |
5. |
Did the decedent own an interest in any real estate as a life estate including a dower interest? |
YES |
NO |
5 |
6. |
ToTal value of nonprobaTe real esTaTe (add lies 1 through 5 above) |
|
6 |
|
pArt 3: summAry of probAte Assets |
|
|
|
|
Complete PART 4 irst. Enter the total from each schedule of PART 4 on the appropriate line below. |
mArket VAlue |
|||
1. |
Schedule A: Real estate or any interest therein |
|
1 |
|
2. |
Schedule B: Tangible personal property of every kind |
|
2 |
|
3. |
Schedule C: Government bonds and securities of every kind |
|
3 |
|
4. |
Schedule D: Shares of corporate stock of every kind |
|
4 |
|
5. |
Schedule E: Money, certiicates of deposit, notes, accounts, etc |
|
5 |
|
6. Schedule F: All other assets not hereinbefore mentioned |
|
6 |
||
7. ToTal value of probaTe asseTs (add lines 1 through 6 above) |
|
7 |
||
Form ET 6.01 |
West Virginia State Tax Department |
Page 1 |
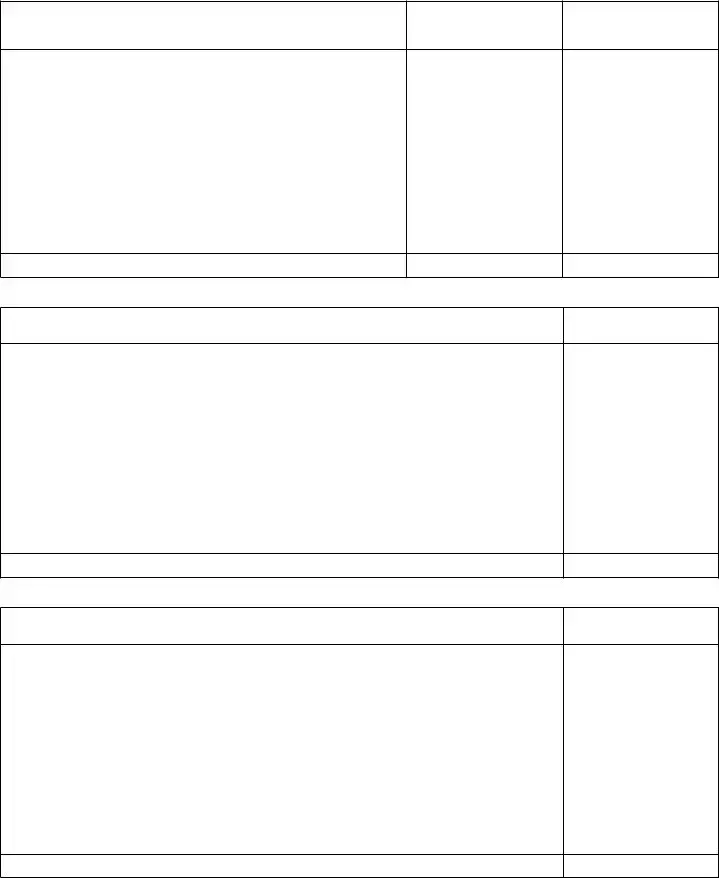
pArt 4: inVentory of probAte Assets – trAnsfers by Will or intestAcy After completing PART 4, enter the total from each schedule on the appropriate line in PART 3.
scheDule A: Describe any real estate or any interest in real estate. Include description and appraised value of out of state property, but do not include this amount in the total. See page 3 of the instructions.
AssesseD
VAlue
ApprAiseD
VAlue
totAl (enter the total appraised value on line 1 of PART 3)
scheDule b: Tangible personal property of every kind. See page 3 of the instructions.
ApprAiseD
VAlue
totAl (enter the total appraised value on line 2 of PART 3)
scheDule c: Bonds and securities of every kind. See page 3 of the instructions.
ApprAiseD
VAlue
totAl (enter the total appraised value on line 3 of PART 3)
Form ET 6.01 |
West Virginia State Tax Department |
Page 2 |
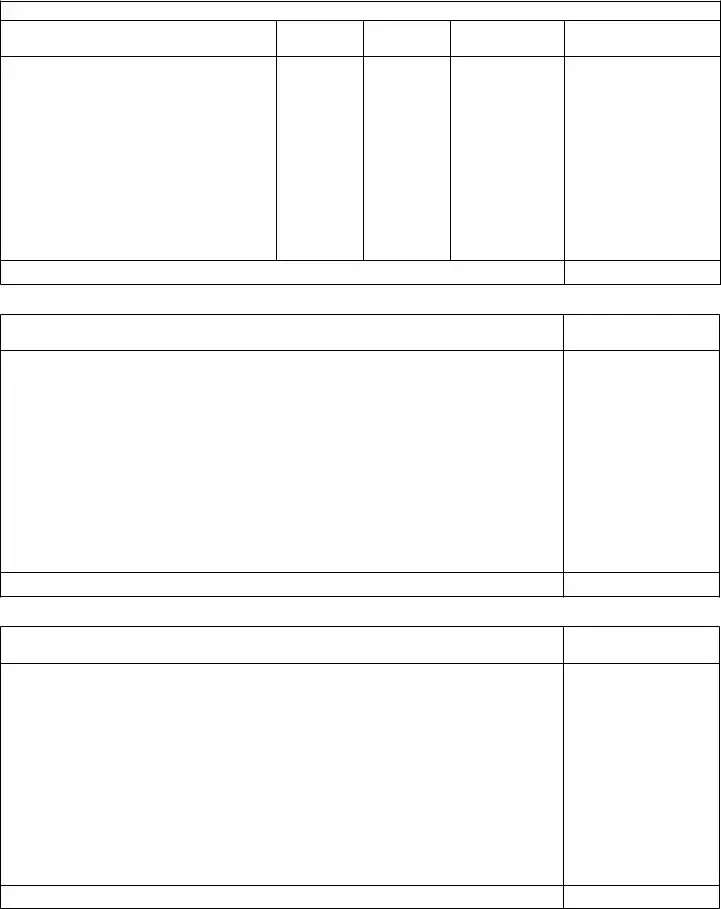
pArt 4 (continued)
scheDule D: Corporate stock of any kind. See page 3 of the instructions.
nAme of the compAny
closely
helD
number
of shAres
mArket VAlue
per shAre
totAl
mArket VAlue
totAl (enter the total market value on line 4 of PART 3)
scheDule e: Money, bank accounts, certiicates of deposits, notes, accounts receivable, etc. Show dates of notes. See page 3 of instructions.
ApprAiseD
VAlue
totAl (enter the total appraised value on line 5 of PART 3)
scheDule f: All other assets, not hereinbefore mentioned, including insurance payable to the estate. See page 3 of the instructions.
ApprAiseD
VAlue
totAl (enter the total appraised value on line 6 of PART 3)
Form ET 6.01 |
West Virginia State Tax Department |
Page 3 |
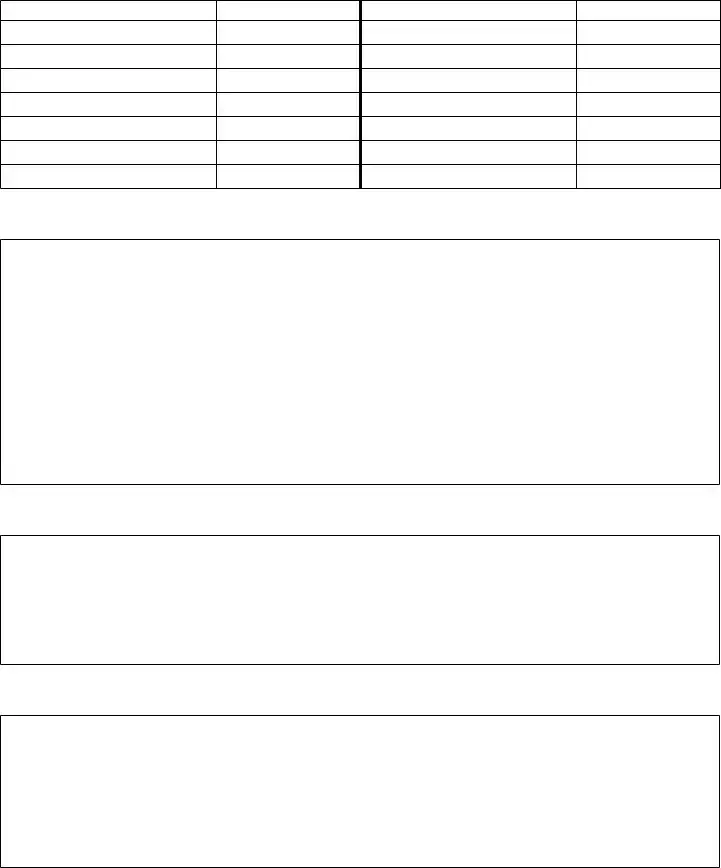
pArt 5: beneficiAries. List the names and relationships of all beneiciaries or heirs of the estate. Show the age of any life tenant after their name. See page 3 of the instructions.
beneficiAry or heir
relAtionship
beneficiAry or heir
relAtionship
pArt 6: oAth of fiDuciAry
State of _______________________________________ County of ______________________________________,
I, __________________________________, iduciary for the estate of __________________________________________
after diligent effort to ascertain the taxable property of this estate, have made answers to each of the questions and have completed, in detail, the schedules for each category of property and believe each item thereof to be correct. I thereby believe the foregoing to be the true and lawful appraisement of ALL real estate and probate property of the estate of the above named decedent.
___________________________________________________________
Fiduciary
Subscribed and sworn to before me this ____________ day of _______________________, 20________
___________________________________________________________
Notary Public
My Commission expires _________________, 20________
pArt 7: ApproVAl of fiDuciAry commissioner/fiDuciAry superVisor
I, ________________________, Fiduciary Commissioner/Fiduciary Supervisor of ___________________________ County,
West Virginia, to whom the estate of the above named decedent was referred, do hereby approve the foregoing appraisement of such estate.
Given under my hand this ___________ day of _________________________, 20______________
________________________________________________ |
By ______________________________________________ |
Fiduciary Commissioner/Fiduciary Supervisor |
Deputy |
pArt 8: clerk of the county commission
STATE OF WEST VIRGINIA
COUNTY OF _________________________________,
In the Clerk’s ofice of _____________________ County on the ________ day of ______________________, 20__________,
the forgoing appraisal of the above named decedent was presented and upon motion admitted to record. Attest___________________________________________, Clerk
By____________________________________________, Deputy
Form ET 6.01 |
West Virginia State Tax Department |
Page 4 |
Decedent’s Name: ____________________________________________________________________________________________
inVentory of nonprobAte reAl estAte
If you answered “YES” to any question under PART 2: QUESTIONNAIRE OF NONPROBATE REAL ESTATE, show the following on this page:
a.the type of transfer(s) with reference to the question number in PART 2;
b.name(s) of the person(s) with an interest in the real estate as joint tenant or transferee;
c.relationship to the decedent of ALL above named persons;
d.market value at the date of death; and
e.description of the real estate including assessed value.
Form ET 6.01 |
West Virginia State Tax Department |
Page 5 |
Form ET 6.02 |
nonprobAte inVentory of the estAte |
Rev. 06/14 |
for DeceDents Dying on or After July 13, 2001 |
|
|
pArt 1: generAl informAtion QuestionnAire
A. Decedent’s Name
B. Social Security Number
C. Date of Death
D. Decedent’s Residence at Death
E. State
F. County
G. Marital Status at Death Married |
Name of Surviving Spouse _________________________ Single, Widow(er) or Divorced |
H. Fiduciary’s Name and Mailing Address (include zip code)
________________________________________________
________________________________________________
________________________________________________
________________________________________________
Fiduciary’s Phone Number:
I. Preparer’s Name and Address CPA  Attorney
Attorney 
________________________________________________
________________________________________________
________________________________________________
________________________________________________
Preparer’s Phone Number:
pArt 2: QuestionnAire of nonprobAte personAl property
Answer each of the following questions concerning the decedent’s interest in NONPROBATE PERSONAL PROPERTY. Nonprobate personal property means all property which does not pass by operation of the decedent’s will or by the laws of intestate descent and distribution or is otherwise not subject to administration in a decedent’s estate.
Note: All real estate and probate property are to be reported on the Appraisement of the Estate (ET 6.01) iled with the County Commission.
if you answer “yes” to any question below, you must complete pArt 3 of this form which shows:
a.the type of transfer(s) with reference to the question number below;
b.name(s) of the person(s) with an interest in the property as joint tenant or transferee;
c.relationship to the decedent of ALL above named persons;
d.market value at the death; and
e.description of the property.
mArket VAlue
1. |
Did the decedent possess any powers of appointment? |
YES |
NO |
1 |
2. |
Did the decedent make any gifts or transfers without adequate consideration within three years prior to the date |
|
|
|
|
of death? |
YES |
NO |
2 |
3. |
Did the decedent make any transfers in Trust which passed to others upon his death? |
YES |
NO |
3 |
4. |
Did the decedent own any stock, bonds, bank accounts, certiicates of deposit or other personal property as a |
|
|
|
|
joint tenant with the right of survivorship? |
YES |
NO |
4 |
5. |
Did the decedent own any life insurance policies to named beneiciaries? |
YES |
NO |
5 |
6. |
Did the decedent own any annuities? |
YES |
NO |
6 |
7. |
Did the decedent own an interest in any personal property as a life tenant? |
YES |
NO |
7 |
8. |
Did the decedent own any personal property which was payable on death to others? |
YES |
NO |
8 |
9. |
Did the decedent ile any Federal Gift Tax Returns with the IRS or make any taxable gifts under Federal Gift Tax |
|
|
|
|
law or regulations? |
YES |
NO |
9 |
10. Did the decedent own any other nonprobate personal property includible in the federal gross estate of |
|
|
|
|
|
a decedent? |
YES |
NO |
10 |
11. ToTal value of nonprobaTe personal properTy (add lines 1 through 10 above) |
|
11 |
||
Form ET 6.02 |
West Virginia State Tax Department |
Page 1 |
Document Specifics
| Fact Number | Fact Detail |
|---|---|
| 1 | The booklet is provided by the Tax Account Administration Division of the West Virginia State Tax Department. |
| 2 | It is intended for estates and decedents dying on or after July 13, 2001. |
| 3 | The book covers the administration of the estate, including filing inventory of all real estate, probate, and nonprobate property. |
| 4 | The Appraisement and Nonprobate Inventory Forms must be filed within 90 days of qualification. |
| 5 | The forms include detailed instructions for inventory of real estate and other assets, including nonprobate personal property. |
| 6 | Part 2 of Form ET 6.01 specifically requires information about nonprobate real estate. |
| 7 | Governing laws include West Virginia Code §42-3A-38 and §44-3-4, especially regarding the fiduciary's role and responsibilities. |
| 8 | The process includes an oath of the fiduciary and review by the County Clerk and potentially a Fiduciary Commissioner or Supervisor. |
Guide to Using West Virginia Estate
Before diving into the process of filling out the West Virginia Estate form, it's crucial to understand the sequence of actions necessary for managing the estate of a decedent. These actions range from recognizing the estate to identifying both probate and nonprobate items. The goal here is to ensure the efficient handling of the decedent's estate, abiding by legal requirements and facilitating a smooth transition. Dealing with an estate can seem overwhelming, but the following steps will guide you through the necessary procedures, ensuring everything is completed accurately and timely.
- Read the instructions carefully for both Form ET 6.01 and Form ET 6.02 provided in the booklet. This step is foundational, as it gives a clear overview of the process and helps avoid any mistakes that could arise from misunderstanding.
- Complete Form ET 6.01 (Appraisement Form):
- Start with Part 1: General Information Questionnaire. Fill in the decedent’s details truly and completely, including their Social Security Number and details concerning their domicile at the time of death.
- Proceed to Part 2: Questionnaire of Nonprobate Real Estate if applicable. Provide details about any real estate owned by the decedent that does not fall under probate. If the decedent owned out-of-state real estate, include these details as well.
- In Part 3: Summary of Probate Assets, compile the total value from each schedule provided in Part 4 of the form.
- Part 4: Inventory of Probate Assets requires a comprehensive listing of all probate assets including real estate, tangible personal property, bonds, corporate stock, intangible personal property, and any other assets. Be thorough and precise.
- Next, complete the section on beneficiaries in Part 5, indicating who will inherit under the decedent’s will or through intestate succession, and their relation to the decedent.
- In Part 6: Oath of Fiduciary, affirm the accuracy of the information provided in the presence of a notary.
- Finally, Part 7 and Part 8 are for official use by the Fiduciary Commissioner/Fiduciary Supervisor and the Clerk of the County Commission, respectively.
- Complete Form ET 6.02 (Nonprobate Inventory Form), if required. This step involves listing and appraising all tangible and intangible nonprobate personal property owned by the decedent.
- Submit the forms to the proper authorities. Delivery options may vary, but typically you will need to deliver the completed Form ET 6.01 and, if necessary, Form ET 6.02 to the fiduciary supervisor or the clerk’s office. Ensure that all accompanying documents and attachments are included.
Completing these steps carefully and within the required time frame is critical to fulfilling your responsibilities as an estate representative. Remember, this process is not only about legality but also about honoring the decedent's legacy by ensuring their wishes and the law are respected.
Essential Points on West Virginia Estate
Who needs to file West Virginia Estate Appraisement and Nonprobate Inventory Forms?
When a person dies, an estate is created which includes property the decedent owned. The law requires that an administrator or executor, known as a fiduciary, files the Appraisement and Nonprobate Inventory Forms within 90 days of qualification to administer the estate by paying the decedent’s debts and distributing the remaining property.
What is the deadline for filing these forms?
The fiduciary must file the Appraisement and Nonprobate Inventory Forms within 90 days of qualification. This is a critical step in the process of administering the estate and ensuring all legal obligations are met.
Is there a requirement for a Federal Estate Tax Return for the estate?
The need to file a Federal Estate Tax Return (Form 706) depends on the gross estate value at the time of death. For 2004 to 2005, estates over $1,500,000 must file, with this threshold increasing in subsequent years up to $5,340,000 for deaths in 2014. It’s important to verify the current exemption equivalent as they are subject to change.
How is real estate included in these forms?
Real estate is considered either probate or nonprobate. Probate real estate must be listed on the Appraisement Form (ET 6.01), while nonprobate real estate is detailed on the Nonprobate Inventory Form (ET 6.02). Nonprobate real estate includes property not passed by will or intestacy laws, such as jointly held property or that held in a trust.
What about nonprobate personal property?
Nonprobate personal property includes items like personal property held as joint tenants with rights of survivorship, life insurance payable to named beneficiaries, assets in trust, and more. This property must be listed on the Nonprobate Inventory Form (ET 6.02) and appraised at its fair market value as of the decedent’s date of death.
Who can serve as an estate’s fiduciary?
Any interested person may administer the estate, but preference is given to the decedent's spouse, then other distributees (those entitled to share in the estate). If no distributee applies within 30 days after the death, creditors or any other person may be appointed. If a will specifies an executor, that individual has the right to serve.
What happens if an estate does not require the filing of an Appraisement and Nonprobate Inventory?
Even if it seems an estate may not require these filings, it’s imperative to consult with the clerk of the county commission or seek legal advice. Certain small estates or those passing entirely through nonprobate means may have different requirements, but verification is key to ensure compliance with West Virginia law.
Can the Fiduciary Commissioner or Fiduciary Supervisor assist in preparing tax returns or reports for the estate?
No, the Fidiciary Commissioner or Fiduciary Supervisor cannot assist in the preparation of a tax return or any other report concerning the estate that they will eventually review or judge. This prohibition extends to practicing law related to an estate under their jurisdiction, following West Virginia Code.
Common mistakes
Filling out estate documentation in West Virginia involves a detailed process that, if not done properly, can lead to complications. One common mistake is the failure to read the provided instructions thoroughly before starting to complete the forms. This oversight can result in misunderstandings about what needs to be included, leading to incomplete or inaccurate submissions. The introductory instructions are designed to guide the fiduciary through the process, ensuring that each part of the form is correctly filled out. It is crucial to review these instructions carefully to understand the scope of the fiduciary's duties and the specifics of what must be documented.
Another frequent error involves incorrectly listing the decedent’s assets. The estate forms require a detailed listing and appraisal of both probate and nonprobate assets at their fair market value as of the decedent's death. Probate assets include all property in the decedent’s name only, while nonprobate assets encompass things like jointly held properties or assets with designated beneficiaries. Mistakes in this area, such as underestimating values, omitting assets, or incorrectly categorizing assets, can significantly impact the administration of the estate and its tax liabilities.
A third misstep is not properly documenting the information required about the decedent's real estate. This includes failure to include nonprobate real estate in the appraisal or inaccurately describing the property. The decedent's interest in real estate, whether probate or nonprobate, must be described thoroughly, including the market value at the date of death. Essential details such as the county, district, physical location, and full appraised value must be accurately recorded. Moreover, if the decedent owned assets in other states, this information must also be provided. Omitting these details or providing incorrect information can lead to an incomplete appraisement.
Lastly, not correctly validating the forms with the necessary signatures is a critical oversight. Both the Estate Appraisement and Nonprobate Inventory Form require the fiduciary's oath, completed in the presence of a notary. This oath affirms that all efforts were made to fully and accurately list the estate's assets. An appraisement without the original signatures of the fiduciary and the notary will not be accepted, which could delay the administration process. Ensuring that all parts of the form are properly signed and submitted on time is essential for the efficient handling of the decedent’s estate.
Documents used along the form
When navigating through the complexities of estate management in West Virginia, it's pivotal to have a comprehensive grasp of the ancillary documents that accompany the West Virginia Estate Appraisement and Nonprobate Inventory forms. These documents are instrumental in ensuring a thorough and lawful administration of the decedent's estate.
- Will or Testamentary Document: This document outlines the decedent’s last wishes regarding the distribution of their assets and the administration of their estate. It nominates an executor to manage the estate affairs.
- Death Certificate: Issued by a governmental body, this legal document certifies the date, location, and cause of a person's death, required for many aspects of estate administration.
- Letters of Administration or Letters Testamentary: These are legal documents issued by the court authorizing the executor or administrator to act on behalf of the estate.
- Fiduciary Income Tax Returns (IRS Form 1041): This form reports the income, deductions, and credits of a decedent's estate during the fiscal year.
- Federal Estate Tax Return (IRS Form 706): Required for estates exceeding certain values, this form calculates the estate tax owed to the federal government.
- Notice of Probate: A document that is filed with the probate court and sometimes published in a newspaper, notifying creditors and potential heirs about the administration of the estate.
- Inventory and Appraisement: A detailed list of the estate's assets, including their valuation at the date of the decedent's death, often required by the probate court and tax authorities.
- Settlement or Closing Statement: This document outlines the final distribution of the estate’s assets to the heirs and any payments made to creditors, concluding the estate’s administration.
To encapsulate, comprehending and obtaining the precise documents as required by the legal procedural framework not only aids in the accurate and efficient administration of the estate but also ensures compliance with West Virginia laws and regulations. It's critical for executors and administrators to familiarize themselves with these requirements to fulfil their duties effectively.
Similar forms
The West Virginia Estate Appraisement & Nonprobate Inventory Forms share similarities with a Last Will and Testament document. Both documents deal with the distribution of a decedent’s assets. While the West Virginia forms focus on listing and valuing the assets for tax and legal purposes, a Last Will outlines how a person wishes their assets to be distributed upon death. Each provides critical information for estate administration but from different angles. The Will declares the decedent’s intentions, whereas the appraisement and inventory forms offer a detailed asset snapshot for legal and tax assessment.
A Trust Agreement also bears resemblance to the West Virginia Estate forms, particularly because both involve designating assets to beneficiaries. However, Trust Agreements often bypass the probate process, directly transferring assets to beneficiaries without the need for formal estate appraisal. Even so, the initial appraisement serves a similar purpose to a trust's funding documentation, recording the assets that will eventually be managed or distributed by the trustee.
Probate Court Filings, much like the West Virginia Estate forms, are integral to the estate administration process. Both sets of documents are essential for the orderly distribution of a decedent’s estate, ensuring debts are paid, and assets are allocated according to the law or the decedent’s wishes. The primary difference is that probate filings follow predefined court procedures, while the West Virginia forms pertain specifically to the task of asset valuation and listing for tax purposes.
Executor’s Deeds reflect another document type related to the West Virginia Estate forms. These deeds are used by executors to transfer real property from an estate to a purchaser or beneficiary. This action essentially completes a process that begins with the property's listing and valuation on the appraisement form, highlighting an important step in the property's transfer from the estate to its new owner.
Federal Estate Tax Return (Form 706) parallels the West Virginia Estate Appraisement & Nonprobate Inventory Forms in its focus on estate value. Both document the assets of a decedent for tax appraisal, with the West Virginia form serving a similar function at the state level while Form 706 meets federal requirements. The careful listing and valuation of assets are crucial in both instances to determine tax obligations accurately.
Inventory Forms for Succession or Small Estates are akin to the West Virginia Estate Forms, as both facilitate the administrative process after someone passes away. However, these forms are generally simpler and used for smaller estates or in jurisdictions with simplified succession laws. Similarly, they require listing assets and valuing them, albeit for a more streamlined probate or estate settlement process.
Beneficiary Designation Forms for financial accounts and life insurance share a common goal with the Nonprobate Inventory Form. Both types of documents identify assets that pass outside the will directly to beneficiaries. While beneficiary designations directly transfer specific assets like retirement accounts or insurance proceeds, the Nonprobate Inventory accounts for these items as part of the broader estate documentation.
Transfer on Death (TOD) Deed resembles the nonprobate aspects of the West Virginia Estate forms by allowing real estate to pass directly to beneficiaries without going through probate. Like the other nonprobate assets listed in Form ET 6.02, a TOD deed simplifies the transfer of ownership, but specifically for real estate, indicating who will receive the property after the owner's death.
A Statement of Claim against an estate echoes the necessities found within the West Virginia Estate forms, particularly because both involve identifying and valuing the assets available to settle debts. Creditors use statements of claim to assert rights to an estate’s assets, necessitating accurate estate appraisals to ensure fair debt settlement in adherence to estate law.
Gift Tax Returns (Form 709), similar to the sections of the West Virginia forms discussing transfers and gifts, concerns the documentation of transferred wealth during the decedent's lifetime. While Gift Tax Returns specifically address transfers that might affect the donor's tax obligations, the appraisal and inventory forms might also record such lifetime transfers if they impact estate value or tax considerations.
Dos and Don'ts
When dealing with the West Virginia Estate Appraisement & Nonprobate Inventory Forms, making sure everything is filled out correctly and submitted on time is critical. Here’s a quick rundown of what you should and shouldn't do to ensure the process goes smoothly.
What You Should Do:
- Read all instructions carefully before starting. Understand the requirements for each section of the forms to fill them out correctly.
- Ensure accuracy in reporting all necessary information. Double-check the decedent's full name, social security number, and date of death to ensure they align with the death certificate.
- List all assets at their fair market value as of the decedent's date of death. This applies to both probate and nonprobate assets, including real estate, personal property, and intangible assets.
- Submit the original documents and the required copies within 90 days of qualification to the appropriate authorities. Timeliness is crucial in this process to avoid penalties.
What You Shouldn't Do:
- Don't overlook nonprobate assets. Nonprobate assets must be diligently listed on Form ET 6.02 and include things like jointly owned property or assets with designated beneficiaries outside of the will.
- Don't forget to obtain and include the decedent’s last will and testament, if applicable. If the decedent left a will, it should guide the distribution of the estate.
- Don't guess on asset values. Obtain professional appraisals if you're unsure about the value of certain assets to ensure accuracy in reporting.
- Don't delay in starting this process. Procrastinating can lead to rushed work, mistakes, and missing the 90-day submission deadline, which could complicate the estate settlement.
Handling an estate responsibly involves careful adherence to the guidelines provided by the State of West Virginia. By following these dos and don’ts, fiduciaries can fulfill their duties effectively, ensuring the decedent's assets are accurately appraised and reported, and ultimately distributed according to law.
Misconceptions
Many people find estate management and the associated paperwork daunting, especially when dealing with specific documents like those required in West Virginia. Here are some of the common misconceptions about the West Virginia Estate Appraisement and Nonprobate Inventory Forms that need clarification:
- Misconception #1: The forms are optional and not legally required. In truth, West Virginia law mandates the filing of these forms for the administration of estates and decedents dying on or after July 13, 2001. The law requires fiduciaries to complete and submit these forms within specified deadlines.
- Misconception #2: Only real estate assets need to be reported. Actually, the forms require reporting of all real estate and nonprobate personal property, capturing a wide range of assets beyond just real property.
- Misconception #3: The same information is repeated on both forms. While it may seem repetitive, each form serves a unique purpose. Form ET 6.01 is for the appraisement of probate assets and requires recording with the County Clerk, whereas Form ET 6.02 is for nonprobate assets and is not recorded.
- Misconception #4: Nonprobate assets are irrelevant to estate settlement. On the contrary, nonprobate assets play a pivotal role and must be accurately reported on Form ET 6.02 for a comprehensive overview of the decedent’s assets, even though they pass outside the probate process.
- Misconception #5: Filling out the forms is straightforward and requires no preparatory work. In reality, careful preparation, including gathering detailed information about all assets and understanding their fair market values as of the date of death, is essential before attempting to complete the forms.
- Misconception #6: Anyone can be appointed as an estate representative without preference. While the forms indicate that any interested person may serve, there is indeed a preferential order starting with the spouse, followed by other beneficiaries, and then creditors if no family member applies within 30 days after death.
- Misconception #7: Only an attorney can complete and submit the forms. Although seeking legal advice is highly recommended, the duty of filling out and filing the forms lies with the appointed fiduciary, who may or may not be an attorney.
- Misconception #8: A Federal Estate Tax Return (Form 706) is always required. The necessity of filing Form 706 with the IRS depends on the total value of the estate against the federal exemption equivalent, which has varied over the years.
- Misconception #9: An appraisement is a one-time event with no subsequent duties. Completing and submitting the forms is only the beginning. The estate's administrator or executor must also manage the assets, settle debts, and distribute the remaining property according to the will or state law, which may involve additional filings and legal proceedings.
Understanding these misconceptions is crucial for anyone involved in estate administration in West Virginia, ensuring compliance with state laws and a smoother probate process.
Key takeaways
Filling out and using the West Virginia Estate form correctly is essential for representatives of an estate. This process requires careful attention to detail, an understanding of the estate's assets, and knowledge of legal and tax implications. To aid in this task, here are key takeaways to ensure the process is handled efficiently:
- Before starting the forms, read the instructions thoroughly. The booklet provided by the West Virginia State Tax Department offers detailed guidance on filling out the Appraisement and Nonprobate Inventory Forms for decedents who passed away on or after July 13, 2001.
- The fiduciary (administrator or executor) must file Appraisement Form ET 6.01 and, if required, Nonprobate Inventory Form ET 6.02 within 90 days of qualification. This timeline is crucial to comply with state requirements and avoid penalties.
- To determine who can serve as a fiduciary, the individuals interested in administering the estate must visit the Clerk's office in the county where the decedent lived. Priority is given to the decedent’s spouse, followed by other distributees and, if none apply within thirty days after the date of death, creditors or other individuals may be appointed.
- Inventories require detailed listings of both probate and nonprobate assets. For probate assets, a complete description and fair market value as of the decedent’s death date must be included. Nonprobate assets must also be listed with fair market values for each item.
- Accuracy in completing the forms is paramount. The fiduciary is responsible for listing and appraising the estate’s assets truthfully and accurately, under oath. Any omission or misrepresentation can lead to legal and financial repercussions.
- Delivery of the forms to the proper authorities varies depending on the county’s processes; in counties with a fiduciary supervisor, the forms (including attachments) are delivered to that supervisor, who then forwards them to the Clerk’s office. In counties without a fidiciary supervisor, the fiduciary must take the forms directly to the Clerk's office.
In navigating these steps, the fiduciary plays a crucial role in ensuring the decedent's wishes are honored and the estate is administered according to West Virginia law. Proactive communication with legal, tax, and estate professionals can provide additional support and guidance through the process.
Popular PDF Forms
West Virginia Board of Accountancy - July 1 to July 31 late filers must include an additional $50 with their renewal form to the West Virginia Board of Accountancy.
Help With Electric Bill in Wv - It includes a section for personal identification, such as name, address, and detailed household composition, including total monthly income before deductions.